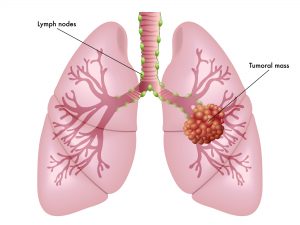
Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer
Higher Risk of Serious Lung Disease (Smoking History and Asbestos Exposure)
Lung Disease Monitoring Opportunity -Age 65 And Above:
If you are age 65, have had 5 years shipyard work before 1982 and smoked or quit smoking within the last 15 years, contact Williams Law Group about access to this NO COST CT scan program. CT scans can identify and help diagnose smaller lung spots. Asbestos exposure creates a higher lifetime risk for cancer development; Asbestos exposure and a history of smoking, together create a multiplicative higher risk.
Previous Asbestos Exposure
Severe Asbestosis, Lung Cancer, or Mesothelioma: If you, or a loved one, worked in a shipyard, construction, or industrial job where you were exposed to asbestos insulation dust and you were diagnosed with severe asbestosis, lung cancer, or mesothelioma within the last three years, you may be entitled to significant cash compensation. Call 601-707-3492 today (or submit the online form below) for a no-cost claim evaluation.
Does Asbestos Cause Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is the deadliest form of cancer in the United States, killing more Americans than colon, prostate, and breast cancer combined each year. In addition, lung cancer associated with asbestos causes about 6,000 deaths annually in the U.S.
Of the lung cancer cases, asbestos is responsible for only a small percentage, but exposure can increase the risk of lung cancer in both smokers and non-smokers. Tobacco smoking is heavily responsible, causing about 80% of lung cancer deaths in the United States.
Asbestos-related lung cancer and pleural mesothelioma are caused by inhaling asbestos fibers. After many years, the lodged fibers can cause immense genetic and cellular damage, enough to turn lung cells into cancer cells. There are two type of asbestos lung cancer: small cell and non-small cell lung cancer. About 18% of lung cancer patients survive more than five years after diagnosis.
Asbestos Lung Cancer Facts
Symptoms include shortness of breath with activity, pain in your chest, annoying cough, repeated respiratory infections, coughing up blood, loss of appetite, weight loss.
Asbestos lung cancer takes decades to develop. Individuals may not have any symptoms until 15 to 35 years after asbestos exposure. Because of this, present cases were caused by past asbestos exposure when asbestos use was common.
Certain professions are at a high risk for asbestos-related lung cancer. These include mining, construction, heavy industry, shipbuilding and firefighting. The military uses asbestos products which makes Veterans a part of the high-risk group.
According to an international study published in 2020, no substance causes more cases of lung cancer linked to occupation than asbestos. The study found that asbestos is responsible for 37.5% of all occupational lung cancer cases.
According to the American Lung Association, only 18% of lung cancer patients survive more than five years after their diagnosis. Compared this to the survival rate for breast cancer of approximately 89% and 98% for prostate cancer.
The two main forms of cancer from asbestos are small cell and non-small cell.
The prognosis and treatment of your cancer will depend on the type and stage of the cancer.
Types of Lung Cancer
There are two primary forms of lung cancer: small cell and non-small cell. Asbestos exposure can be associated with both forms of lung cancer.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) makes up about 85% of all lung cancer cases. They are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy and are usually treated by surgery resection. There are three subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer are squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinomas begin in the tissues that line the airways of the lungs. It accounts for about 25% to 30% of all lung cancers. It is also known as epidermoid carcinoma.
Large cell (undifferentiated) carcinoma is made up of epithelial cells that tend to infiltrate surrounding tissue, can appear in any part of the lung, and spreads more rapidly than the other subtypes of NSCLC. These large cell carcinomas make up about 10% to 15% of all lung cancers.
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of cancer in non-smokers. It forms in mucus-producing glandular tissues that line the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. accounting for about 40% of cases.
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) makes up 10% to 15% of cases. Small cell lung cancer can grow rapidly and can spread before symptoms arise, making it more difficult to treat. Chemotherapy is normally the treatment for this type of cancer.
How Does Asbestos Cause Lung Cancer?
Risk factors for asbestos lung cancer include:
People who are exposed to asbestos for long periods of time
Your personal genetic makeup
Your smoking history will play a big role in asbestos caused cancer if coupled with asbestos exposure
Your overall health will also contribute to how well you handle a cancer diagnosis
Asbestos-Related Lung Cancer and Smoking
Because smoking impairs the lungs’ ability to remove asbestos fibers, the risk of lung cancer is much higher if exposed to asbestos. Smokers should immediately stop smoking and get yearly screenings for lung cancer.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Whether lung cancer is associated with asbestos exposure, smoking, or another cause, it presents the same general symptoms:
Persistent coughing
Shortness of breath
Chest discomfort or pain
Hoarseness or wheezing
Coughing up blood
Fatigue and loss of appetite
Swelling of the face or neck
Chronic respiratory infections
These symptoms only arise once the cancer has developed and is tougher to treat. People with a history of asbestos exposure need regular screenings for asbestos-related diseases.
How Is Asbestos Lung Cancer Diagnosed?
The diagnostic process starts with X-rays and CT scans for images. A pathologist then examines a biopsy sample of questionable tissue and determines if it is a lung cancer diagnosis.
The biopsy is extracted with a bronchoscope or through a long needle and is passed down the throat into the lungs’ airways.
Lung Cancer Treatment
Depending upon the type of cancer and how far it has spread, there are several treatments for lung cancer.
Chemotherapy – is used to kill the cancer cells to prevent the spread of the cancer. One or more anti-cancer drugs can be used. It can be used to lessen the symptoms or prolong life.
- Radiation Therapy – is a therapy that may be used by administering ionizing radiation as a part of a patient’s treatment to kill the malignancy.
Immunotherapy – can be used as a treatment for cancer by activating or suppressing the immune system.
Surgery – can be used to remove the malignancy.
Call Williams Law Group Today
Office:
228-219-7888
Asbestos Lung Disease
& Other Cases: 601-707-3492
Contact Us
912 Convent Ave.
Pascagoula, MS 39567